
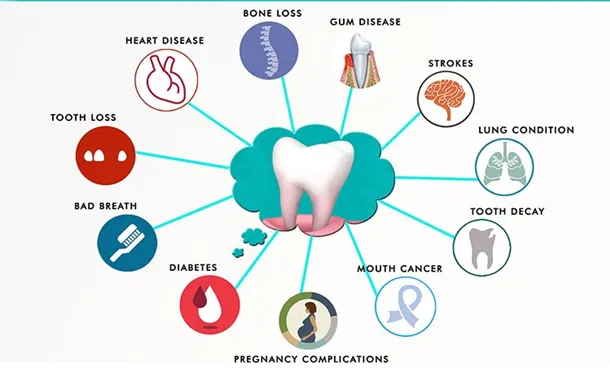
Dental care and the link between oral health and overall health is a crucial aspect of preventative medicine. A healthy smile often masks a healthy body! This guide delves into the intricate connection between what happens in your mouth and your overall well-being. Understanding this connection is key to proactive health management and achieving a healthier life. This comprehensive guide will explore the various ways in which oral health directly impacts systemic health, from heart disease to diabetes. We’ll cover crucial aspects of daily oral hygiene, the importance of regular checkups, and lifestyle factors that impact your oral well-being. We’ll also explore how you can make informed decisions for a healthier you. Let’s begin exploring this powerful relationship and discover the path to better overall health.
The Intertwined Nature of Oral and Systemic Health
The Mouth-Body Connection
Oral health is not an isolated entity; it’s deeply intertwined with the rest of your body. The bacteria and inflammation present in the mouth can trigger or exacerbate systemic conditions like heart disease, stroke, and even diabetes. A direct pathway exists between the inflammatory processes in the mouth and the inflammatory processes that may affect other parts of the body.
The Role of Oral Bacteria
The human mouth is a complex ecosystem teeming with various bacteria, some beneficial, some harmful. An imbalance in this delicate ecosystem can lead to inflammation and potential consequences beyond the mouth. Gum disease, for example, is characterized by the chronic inflammation of the gums, which can significantly impact overall well-being.
The Inflammatory Cascade
Research suggests a strong link between chronic inflammation and systemic diseases. The inflammatory processes initiated by oral bacteria can enter the bloodstream and contribute to widespread inflammation throughout the body. This can increase the risk of various diseases.
Preventing Gum Disease
Effective Oral Hygiene
Maintaining optimal oral hygiene is paramount for preventing gum disease and the systemic issues it can trigger. Daily brushing and flossing are fundamental practices, ensuring food particles and plaque are removed to prevent infection. Using fluoride toothpaste is also important in remineralizing enamel and strengthening tooth surfaces.
Regular Dental Check-ups
Professional dental cleanings and check-ups are essential for early detection and treatment of potential issues. Dental professionals can identify developing gum disease or other problems early on when intervention is most effective and preventative.
Addressing Underlying Conditions
Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, can increase the risk of gum disease. Management of underlying conditions can significantly reduce the risk of oral health problems, enhancing both oral and overall health.
The Impact on Cardiovascular Health
The Gut-Brain-Heart Axis
Research increasingly highlights the complex relationship between the gut microbiome, the brain, and the heart. Oral bacteria can affect gut health, impacting the gut-brain-heart axis and potentially affecting cardiovascular health.
Inflammation and Blood Vessels
Inflammation triggered by gum disease can influence cardiovascular risk factors. Studies show a correlation between periodontal disease and an increased risk of heart disease and stroke, suggesting a potential inflammatory link.
The Role of Plaque
Plaque buildup in the mouth harbors bacteria that release toxins into the bloodstream, impacting blood vessel function and potentially increasing blood clotting risk. This emphasizes the direct impact oral health has on cardiovascular well-being.
Dental Care and Diabetes
The Double-Edged Sword
Diabetes can significantly increase the risk of developing oral health problems, including gum disease. The high glucose levels often associated with diabetes can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to oral infections.
Gum Disease and Insulin Resistance
Gum disease can also impair glucose control. The chronic inflammation associated with gum disease can exacerbate insulin resistance. Maintaining good oral health is crucial in managing diabetes effectively.
Treatment for Diabetic Patients
Proper oral hygiene and routine checkups are crucial to maintain oral health for patients with diabetes. A comprehensive oral care plan can help manage diabetic conditions and improve the overall health outcomes of these patients.
Nutritional Factors and Oral Health
The Role of Diet
A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients plays a vital role in supporting oral health. Fruits, vegetables, and whole grains are crucial for promoting healthy gums and teeth.
Reducing Sugar Intake
Excessive sugar intake can contribute to tooth decay and increase the risk of gum disease. Minimizing sugary beverages and snacks can significantly improve oral health.
Hydration and Oral Health
Drinking plenty of water helps keep the mouth moist, which can prevent tooth decay and gum problems. Keeping the mouth moist is important in maintaining overall oral health.
In conclusion, maintaining excellent dental care isn’t just about a dazzling smile; it’s a crucial aspect of overall well-being. Prioritizing oral hygiene, regular check-ups, and a balanced diet are essential steps towards a healthier you. Schedule a consultation with your dentist today to discuss personalized preventative strategies and learn more about the profound link between oral health and overall health. Your journey to optimal health starts with a healthy smile!