Gum disease, a common oral health concern, affects millions worldwide. Characterized by the inflammation and infection of the gums, it can lead to a range of discomfort and, if left untreated, serious complications. This article dives deep into the struggle with gum disease, exploring the causes, symptoms, and crucial treatment approaches for effectively managing and preventing the condition. We’ll cover everything from recognizing bleeding and swelling to understanding the importance of professional dental care. We’ll guide you through a comprehensive understanding of this widespread condition, offering practical solutions for maintaining healthy gums.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Gum Disease
Types of Gum Disease
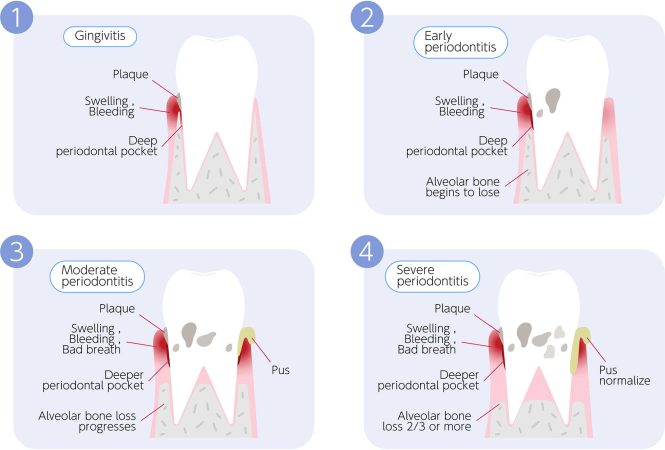
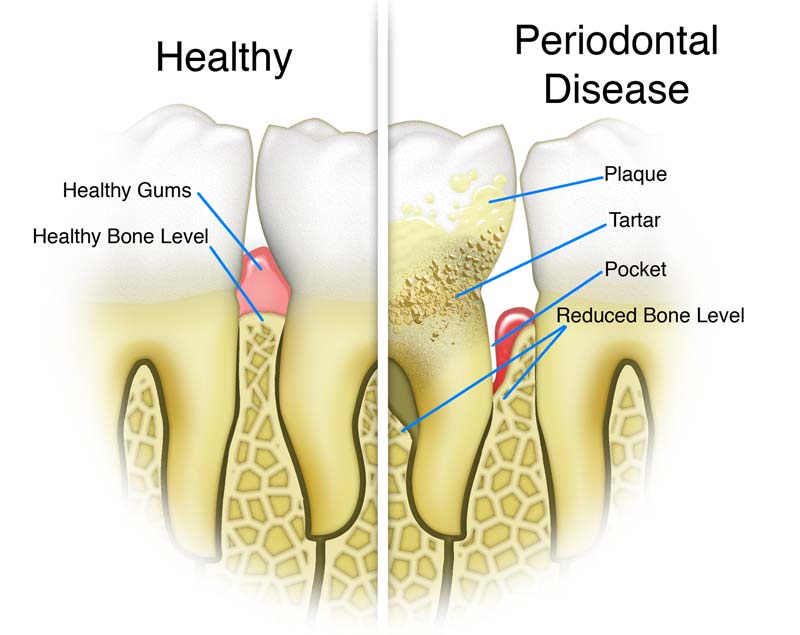
Gum disease, encompassing a spectrum of inflammatory conditions, falls broadly into two primary categories: gingivitis and periodontitis. Gingivitis, the initial stage, typically manifests with mild inflammation and bleeding gums, often triggered by poor oral hygiene. Left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a more severe condition involving the destruction of the supporting tissues that hold your teeth in place. This irreversible condition can lead to significant issues if not identified and treated in a timely manner.
Risk Factors and Predispositions
Numerous factors increase the risk of gum disease, including poor oral hygiene practices, smoking, diabetes, certain medications, genetic predisposition, and nutritional deficiencies. Maintaining a consistent oral hygiene routine and scheduling regular dental checkups are essential in managing the risk factors. A balanced diet rich in essential vitamins and minerals can also play a vital role in oral health, reducing the likelihood of gum disease.
Identifying the Symptoms of Gum Disease
Recognizing the Early Warning Signs
Common symptoms of gum disease include bleeding gums, especially during brushing or flossing. Swollen, tender, or red gums are also frequent indicators. Bad breath or a persistent metallic taste in the mouth can also be warning signs. Additionally, loose teeth and receding gums are more prominent signs of advanced disease. Identifying these early indicators and seeking appropriate care can significantly improve the outcome.
The Importance of Early Detection and Treatment
Early detection and treatment are paramount in managing gum disease effectively. Delaying intervention can allow the condition to worsen, potentially leading to advanced periodontitis. Regular dental checkups can identify any early symptoms, enabling prompt intervention and preventing more serious complications. The proactive approach of consistent dental checkups and a thorough oral hygiene routine are essential for preventative care and oral health maintenance.
The Role of Oral Hygiene in Preventing Gum Disease
Establishing a Comprehensive Oral Hygiene Routine
A comprehensive oral hygiene routine is crucial for preventing gum disease. This includes brushing teeth effectively twice a day for at least two minutes each time, using fluoride toothpaste, and flossing daily to remove plaque and food particles from between teeth. Proper brushing techniques involve gentle circular motions, avoiding aggressive scrubbing that can damage gums. Using an antiseptic mouthwash can further enhance gum health and control bacteria.
The Significance of Regular Professional Dental Care
Regular professional dental care plays an indispensable role in preventing and managing gum disease. Dental checkups and cleanings are critical for removing plaque buildup that can lead to inflammation and infection. A skilled dental hygienist can remove plaque and tartar that can cause discomfort or pain. Regular visits also allow your dentist to detect any early signs of gum disease before they become severe, allowing for prompt and appropriate treatment.
Treatment Options for Gum Disease
Non-Surgical Interventions
For mild to moderate cases of gum disease, non-surgical interventions like scaling and root planing are often effective. Scaling involves removing plaque and tartar buildup above and below the gum line, while root planing smoothes the roots of teeth to prevent further bacterial accumulation. This approach, combined with improved oral hygiene practices, can often resolve the issue.
Surgical Interventions
In cases of advanced gum disease, surgical interventions may be necessary. Gum grafts, for example, can help restore lost gum tissue. Other surgical procedures might involve flap surgery to access and clean deep pockets around teeth, or bone grafting to restore lost bone structure. The selection of the most appropriate treatment approach will depend on the severity and progression of the condition, as determined by a dentist.
Lifestyle Modifications for Healthy Gums
Dietary Considerations for Gum Health
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is essential for supporting overall health, including gum health. Limiting sugary and acidic foods that can contribute to plaque formation is also important. Consider incorporating foods rich in Vitamin C and other nutrients that promote healthy gums.
Stress Management and Oral Well-being
Stress can affect your overall health, including your oral health. Managing stress through relaxation techniques and mindfulness practices can contribute to healthier gums. Stress can compromise the immune system, potentially making you more susceptible to gum disease. Prioritizing stress management alongside oral hygiene can be a proactive approach to oral health maintenance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main causes of gum disease?
Several factors contribute to gum disease, including poor oral hygiene, inadequate flossing, smoking, certain medical conditions like diabetes, and genetics. Poor dietary habits can exacerbate the condition. A professional assessment is crucial to diagnose the underlying factors. Regular dental checkups and effective oral hygiene routines can mitigate the risk and minimize the likelihood of the condition developing.
How can I tell if I have gum disease?
Common signs of gum disease include bleeding gums, swollen gums, red or inflamed gums, bad breath (halitosis), and loose teeth. Receding gums can also be a symptom. It’s essential to consult a dentist for a thorough diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. Early intervention can prevent more severe complications and maintain healthy gums.
In conclusion, managing gum disease effectively involves a proactive approach, including regular dental checkups, meticulous oral hygiene, and a balanced diet. Addressing gum bleeding and swelling promptly can prevent further complications and maintain optimal oral health. Schedule a consultation with your dentist if you experience persistent or severe symptoms. Early intervention is key to preventing more serious issues like periodontitis. By understanding the causes and implementing preventative measures, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing gum disease and enjoy a lifetime of healthy gums.