
Supplement absorption inhibitors play a significant role in how effectively your body utilizes dietary supplements. These inhibitors, frequently found in common foods and beverages, can hinder the absorption of essential nutrients, reducing the efficacy of your supplement regimen. This comprehensive guide explores a variety of supplement absorption inhibitors, providing actionable insights on how to optimize your supplement intake and maximize nutrient absorption. We’ll delve into specific foods and drinks known to interfere with supplement absorption, and explore potential strategies to mitigate these issues. The structure of this article will include a detailed breakdown of common inhibitors, practical tips for avoiding them, and actionable advice to enhance supplement effectiveness.
Common Foods and Drinks That Interfere with Supplement Absorption
Supplement absorption inhibitors can significantly impact the effectiveness of your supplementation regimen. Understanding the specific foods and beverages that act as inhibitors is crucial for achieving optimal health outcomes. Many individuals are unaware of how common foods and drinks interfere with their supplement absorption, potentially leading to reduced efficacy. This section will detail the most common foods and drinks that act as inhibitors and how they impact supplement absorption.
Dairy Products
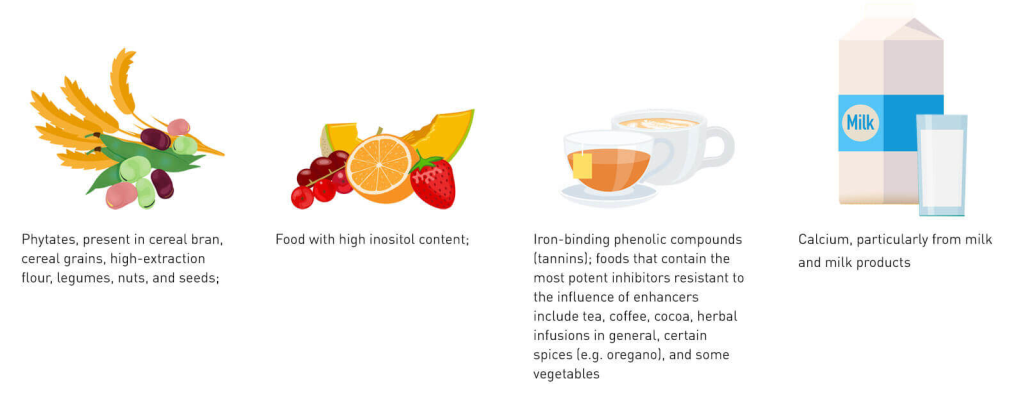
Dairy products, a staple in many diets, contain compounds that can reduce the absorption of certain nutrients, including calcium and iron. Calcium-rich dairy products can interfere with the absorption of iron supplements. For instance, consuming dairy products along with iron supplements can reduce the amount of iron absorbed by the body, potentially leading to insufficient iron intake. Furthermore, certain medications and supplements are often incompatible with calcium-rich foods, and can reduce their absorption, impacting the overall effectiveness.
Coffee and Tea
Coffee and tea contain compounds, including tannins, that can bind to certain minerals, such as iron and zinc, and reduce their absorption. This is particularly relevant for individuals supplementing with these minerals. A study published in the Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism found that consuming coffee alongside iron supplements can reduce iron absorption by 60-80%. Consequently, spacing out consumption of these beverages and supplements may be necessary to avoid this interference.
High-Fiber Foods
High-fiber foods, such as beans, lentils, and whole grains, can interfere with the absorption of certain minerals and nutrients, including zinc, iron, and calcium. The high fiber content can bind to these nutrients, preventing their complete absorption. For optimal absorption, consume these foods separately from your supplements, or consider using supplemental forms of the minerals which are easier to absorb when combined with high fiber foods.
Strategies to Optimize Supplement Absorption
Taking steps to mitigate the interference of common foods and drinks is key to optimizing supplement absorption. By understanding these inhibitors and implementing the appropriate strategies, individuals can enhance supplement efficacy and maximize the benefits they provide. Taking these recommendations with consideration to your particular diet and health needs will have you on the path to optimal supplement outcomes.
Timing Supplements with Meals
Consuming supplements at specific times relative to meals is an important consideration to optimize absorption. High fat meals can enhance the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. Timing supplements based on meal content and type of supplement is critical for improved efficacy. This can greatly affect absorption rate and is a critical strategy to implement.
Selecting Appropriate Supplement Forms
Different supplement forms can affect absorption rates. For example, iron supplements in the form of ferrous bisglycinate can have improved absorption compared to ferrous sulfate. Choosing the appropriate supplement form is important for optimizing the absorption of certain nutrients.
Maintaining a Healthy Gut
The health of your digestive tract is important for ensuring the efficient absorption of nutrients. Maintaining a healthy gut environment can improve overall nutrient utilization and benefit those looking to optimize their supplement intake.
Considering Individual Needs
Recognizing the role of individual differences is important when considering supplement absorption inhibitors. Diet and health history should be taken into consideration to determine the most appropriate strategy for you. Consult with a healthcare professional for tailored advice specific to your needs. This will help maximize your supplement efficacy and prevent potential negative interactions.
In conclusion, understanding supplement absorption inhibitors is crucial for maximizing nutrient absorption and achieving desired health outcomes. By recognizing common foods and drinks that interfere with supplement effectiveness, individuals can optimize their supplement regimens for better results. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best approach for your specific needs and to tailor a personalized supplementation plan that avoids interactions. This will allow you to fully harness the potential of your supplements and achieve your health goals.